- Top Results
- Bosch Building Technologies
- Security and Safety Knowledge
- Security: Video
- Difference between WDR - HDR - HDRX
Difference between WDR - HDR - HDRX
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
WDR
The full name of WDR is Wide Dynamic Range.
WDR is the ratio (in dB) in a scene between the lightest signal value and the darkest signal value that can be distinguished.
The lightest image is caused by overexposure and the darkest image is caused by underexposure.
A high WDR ratio means that bright and dark images in the scene are displayed more clearly at the same time.
It can roughly be said that WDR is enabled through hardware, and it is not a feature that can be turned on or off but a HW capability
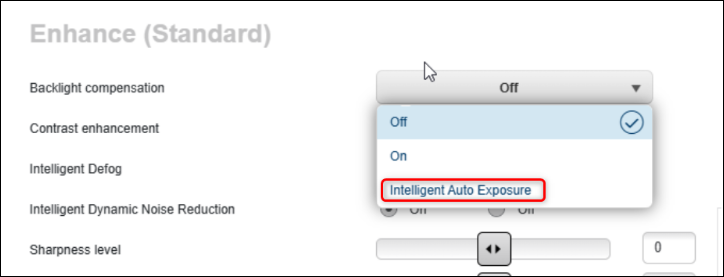
Some cameras have the option to enable "Backlight Compensation" mode called "Intelligent Auto Exposure" which can boost the WDR experience
HDR Bosch traditional High Dynamic Range
The full name of HDR is High-Dynamic Range.
In comparison to WDR that is enabled through hardware , HDR is through software.
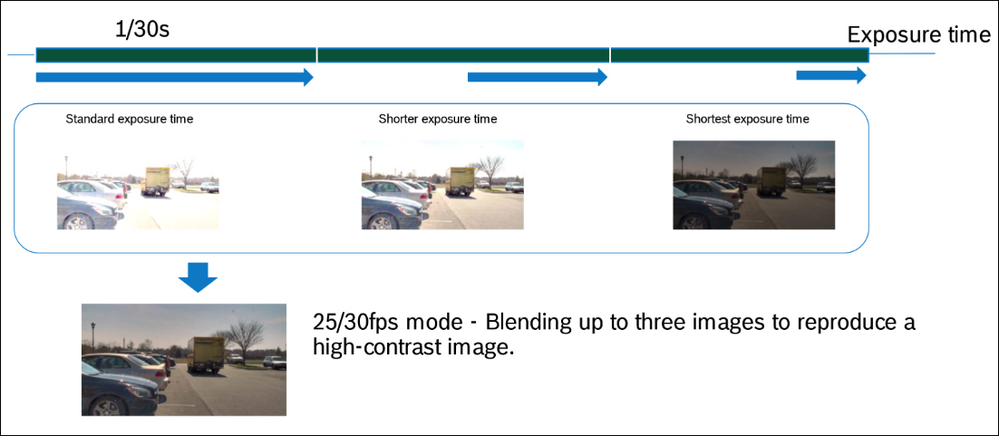
HDR technology combines multiple images with different exposure times to increase the overall dynamic range ensuring the capture of detailed images in scenes that have both light and dark areas.
The time difference between exposures and the total time of the long exposure can result in HDR blur and artifacts with fast-moving objects.
This technique is therefore best applied to predominantly static scenes.
Bosch HDR X
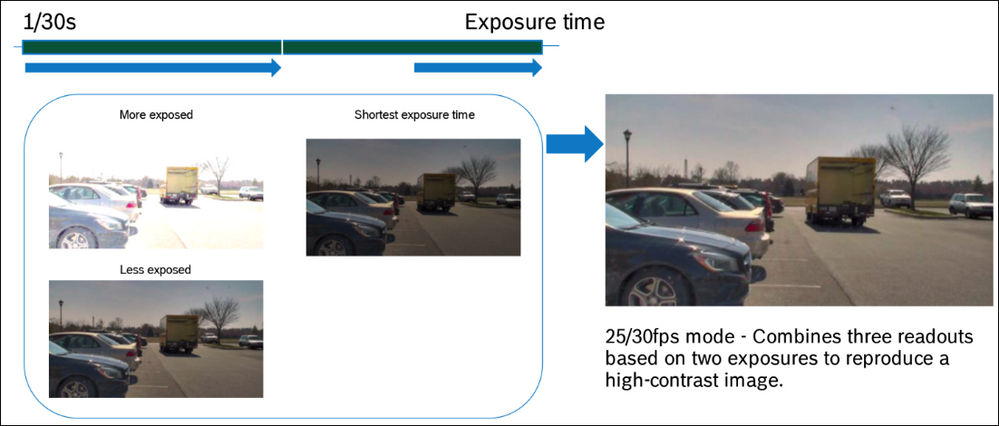
a combination of large pixel sensors, custom-optics, and Bosch imaging algorithms, generates two readouts from one short exposure with different gain levels.
This lens-sensor combination generates a High Dynamic Range frame without any HDR blur and artifacts.
The result is an enhanced dynamic range (up to 144dB) that is motion-optimized to capture the highest level of detail in challenging scenes with both dark and bright areas, while eliminating blur and artifacts caused by the movement of objects.
see also: https://www.boschsecurity.com/xe/en/news/product-news/x-factor-starlight-hdr-technology-explained
Bosch HDR X - Motion Optimized
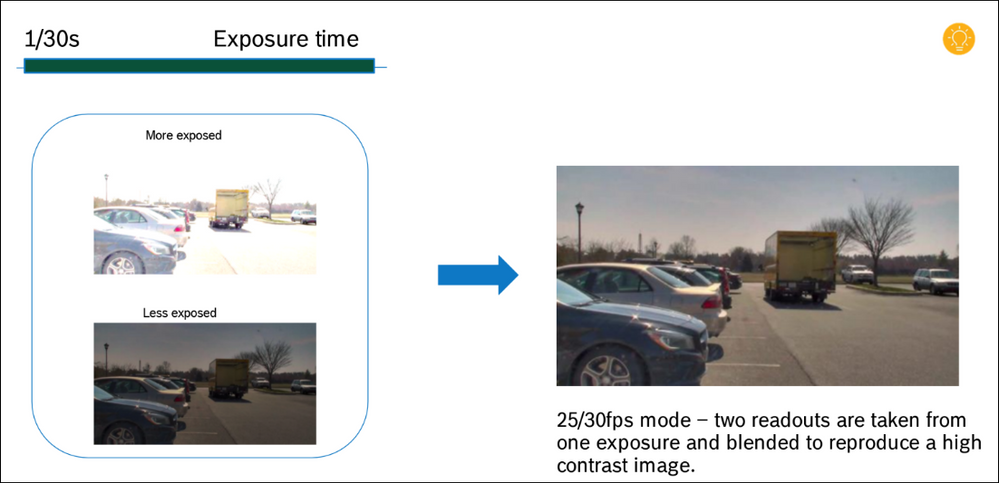
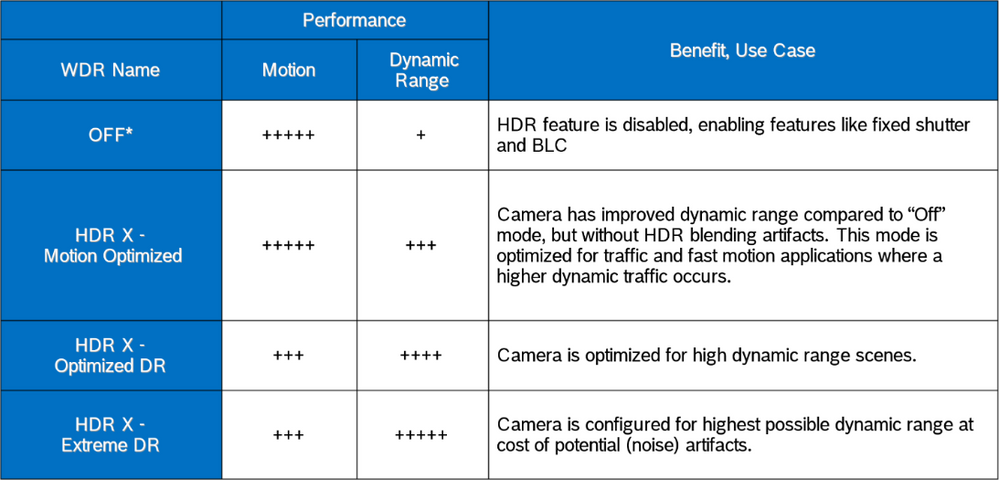
table below is from an AUTODOME IP starlight 5100i
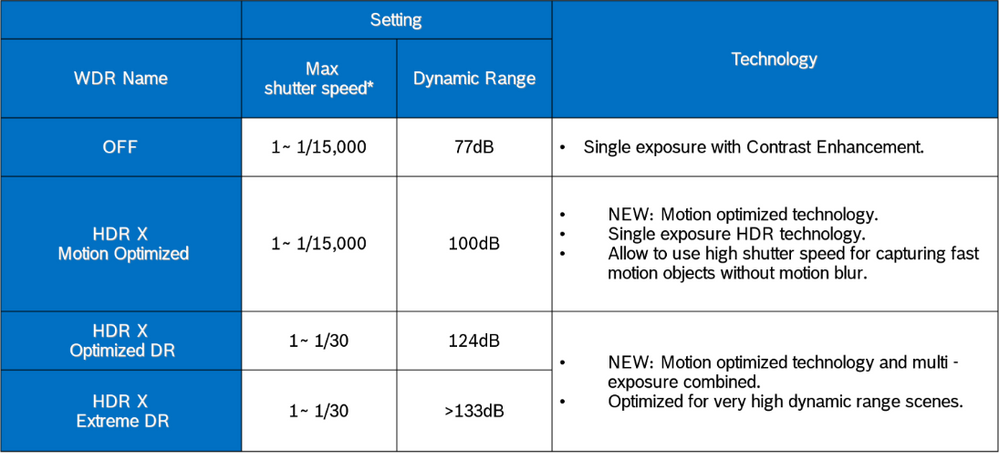
Bosch HDR X - Optimized DR and HDR X - Extreme DR
Still looking for something?
- Top Results