- Top Results
- Bosch Building Technologies
- Security and Safety Knowledge
- Security: Video
- How to configure the Windows Firewall and adjust program rule after BVMS upgrade?
How to configure the Windows Firewall and adjust program rule after BVMS upgrade?
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
This article provides you with information related to the Windows Firewall, how to access, configure and adjust it.
Step-by-step guide
Firewall
A firewall is a program installed on your machine or a piece of hardware in your network, that uses a rule-set to block or allow access to a computer, server or network. It seperatres dedicated network segments, likly your LAN from the Internet. Firewalls can permit traffic to be routed through a specific port to a program or destination, while blocking all other traffic.
Windows Firewall
The Windows Firewall interface can be accessed multiple ways. The way we will look during this TB is via the Windows search function.
Click the Windows icon and type in “firewall“. Then, click on the “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” icon.
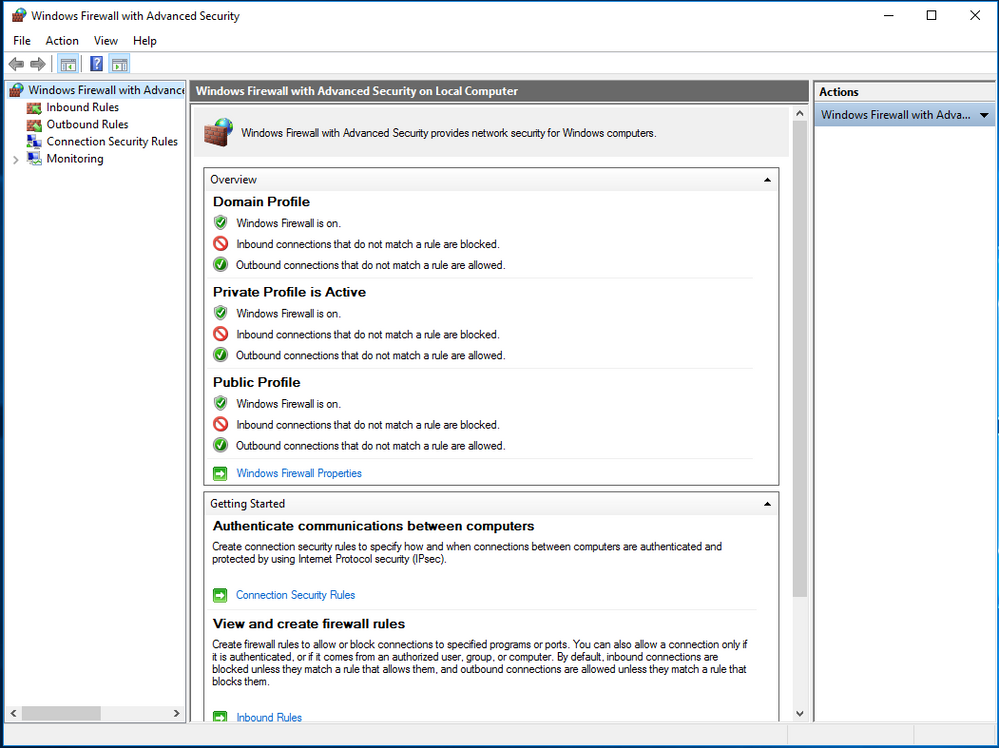
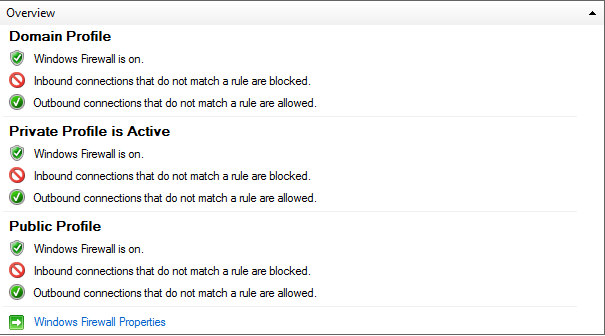
The GUI provides you a general overview, about the basic function of the software. Displaying the current status of the firewall also which profiles are currently set up. By default the firewall should be enabled.
We strongly recommend that the Windows Firewall is enabled on all your Bosch devices featuring a Windows Operating System.
Firewall profiles
There are 3 different profiles within your Windows Firewall, which are simply groups of different firewall rule-sets, depending where your machine is currently connected.
Public Profile: This profile is used when the computer is connected directly to a public network like a restaurant, library or airport. This profile should be the most restrictive because security is usually not well controlled in public places.
Private Profile: This profile is used if your are only connected to a private network, not directly to the Internet. In these cases, your device is located behind a router or hardware firewall. Which allows to set this profil less restrictive.
Domain Profile: This profile is used when the machine is connected to a domain controller, which in turn is controlling a windows domain. This profile should be the least restrictive of the other profiles because security is usually very well controlled within a domain.
Standdard rule-set
by default the Windows Firewall behavior is the following:
- Windows Firewall never blocks outgoing traffic. Any requests sent out from the server will not be hindered in any way.
- Windows Firewall blocks all incoming traffic, except for traffic that is in responses to a request.
This means that if you make a request to Google, Google’s inbound reply to your outbound request will not be blocked. - Windows Firewall blocks all other traffic. This means that any traffic that is not explicitly allowed is blocked in the firewall.
- In the Windows Firewall we can filter connection in two different kinds: port exceptions (rule assigned to a dedicated port number) and program exception (rule assigned to a dedicated program)
In general we need to distinguish between the inbound (frome somewhere to your machine) and outbound (from your machine to somewhere) rule-set.
Open a port in the firewall (inbound rule)
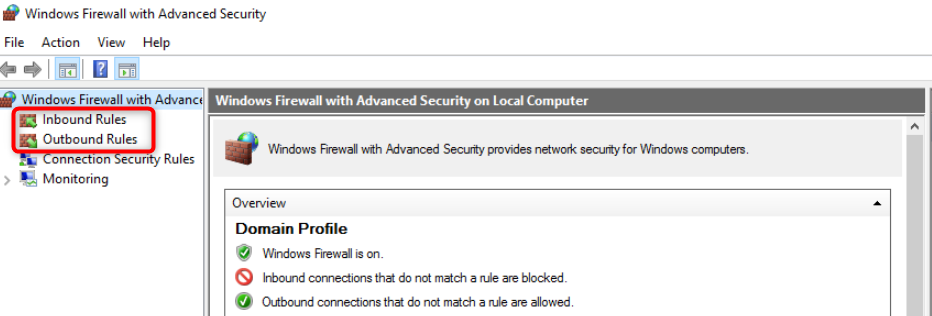
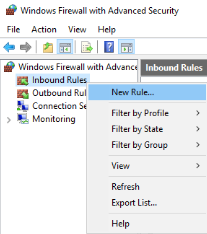
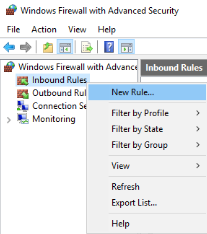
- In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security window, right-click "Inbound Rules", and then click "New Rule..." in the action pane.
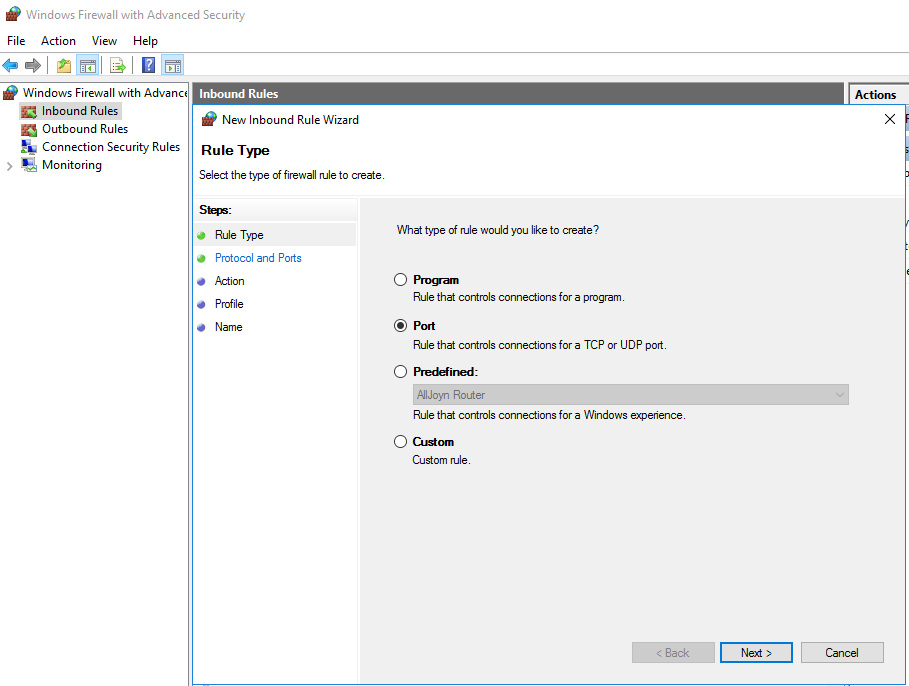
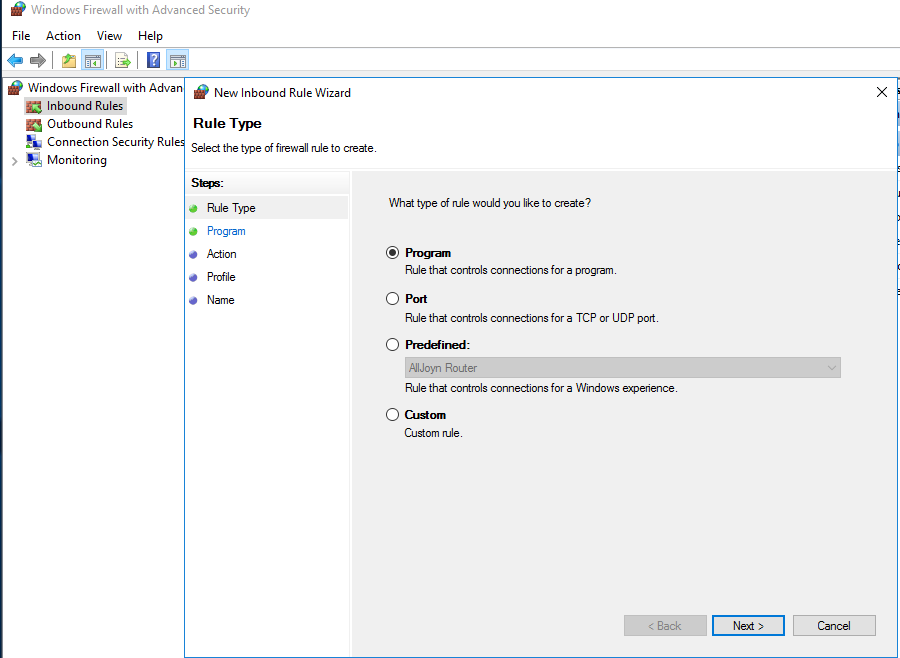
- "Rule Type" dialog box, select "Port" depending on your need and then click "Next".
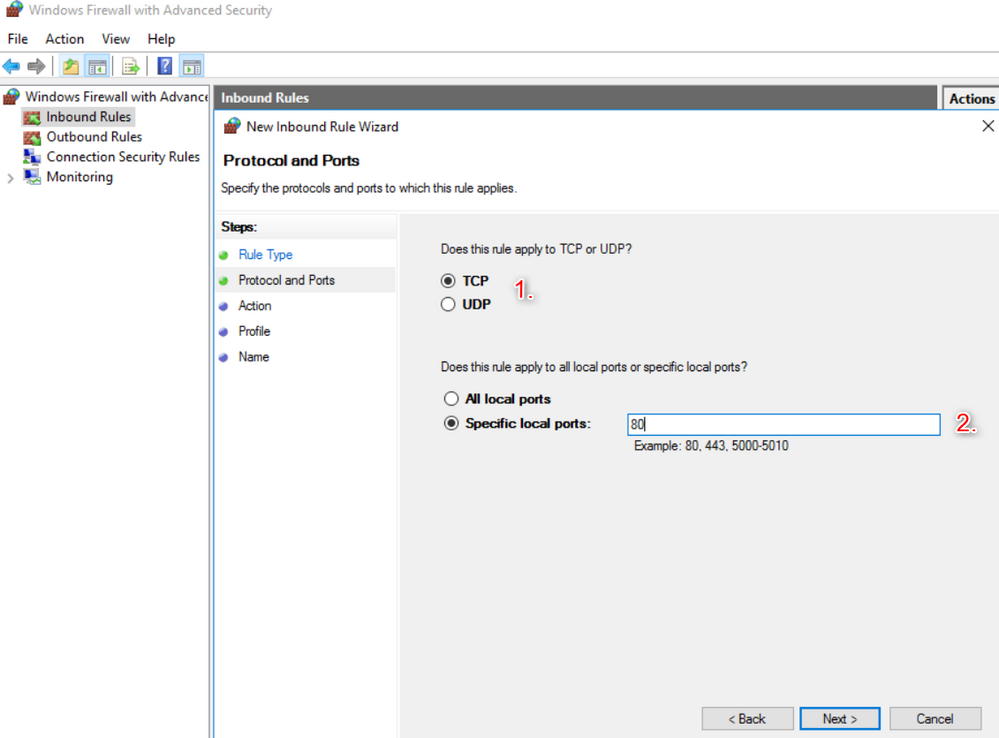
- In the "Protocol and Ports" dialog box, select "TCP". Then select "Specific local Ports", and then type the port number and then click "Next".
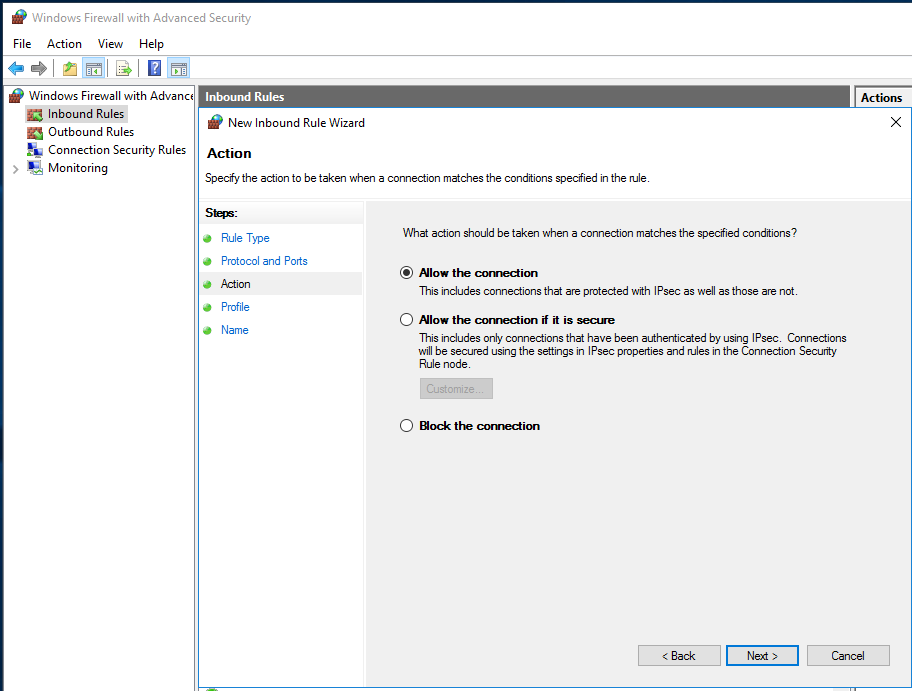
- In the "Action" dialog box, select "Allow the connection" and then click "Next".
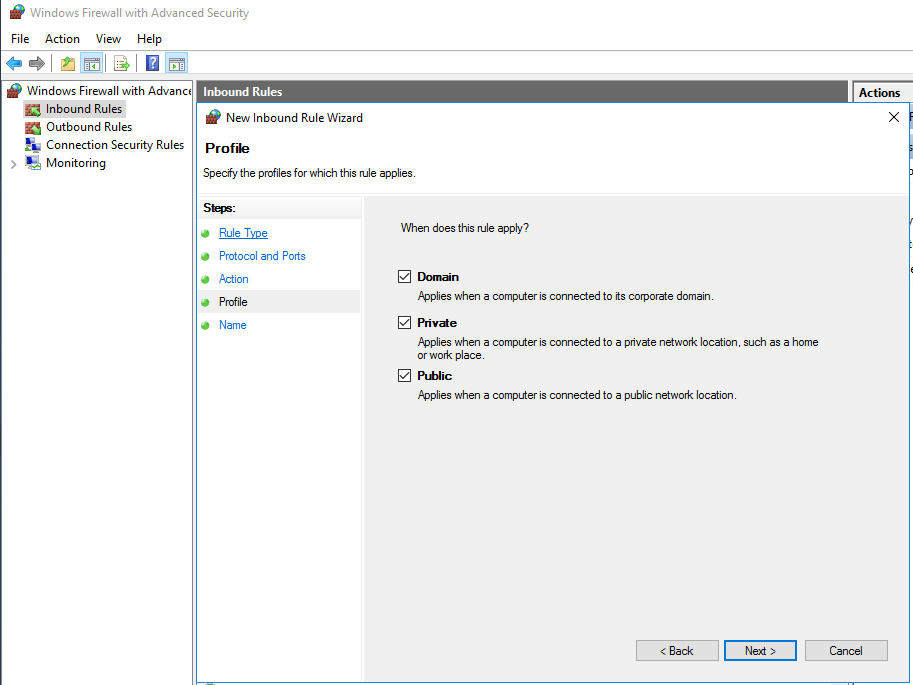
- In the "Profile" dialog box, select any profiles that apply and then click "Next". (We have allowed all three for demonstration purposes, your selection may vary.)
- In the "Name" dialog box, type a name and description for this rule, and then click "Finish".
At this point, you will now see a new rule in the main firewall rules in the center section, as well as a new listing in the right window panel.
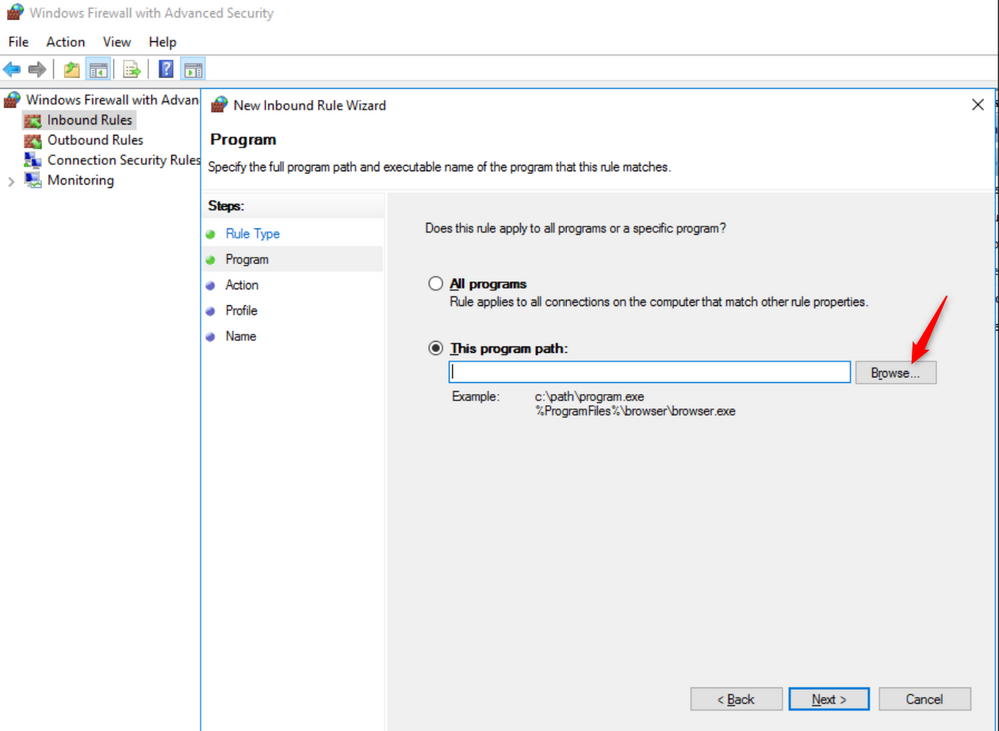
Open a program in the firewall (inbound rule)
- Click on the "Inbound Rules" option on the top left of the firewall interface. Then, click on the "New rule…"
- Under "Rule Type" dialog box, select the option "Program" and then click "Next".
- Select the option "This Program path" browse to the path/location of the program and click "Next".
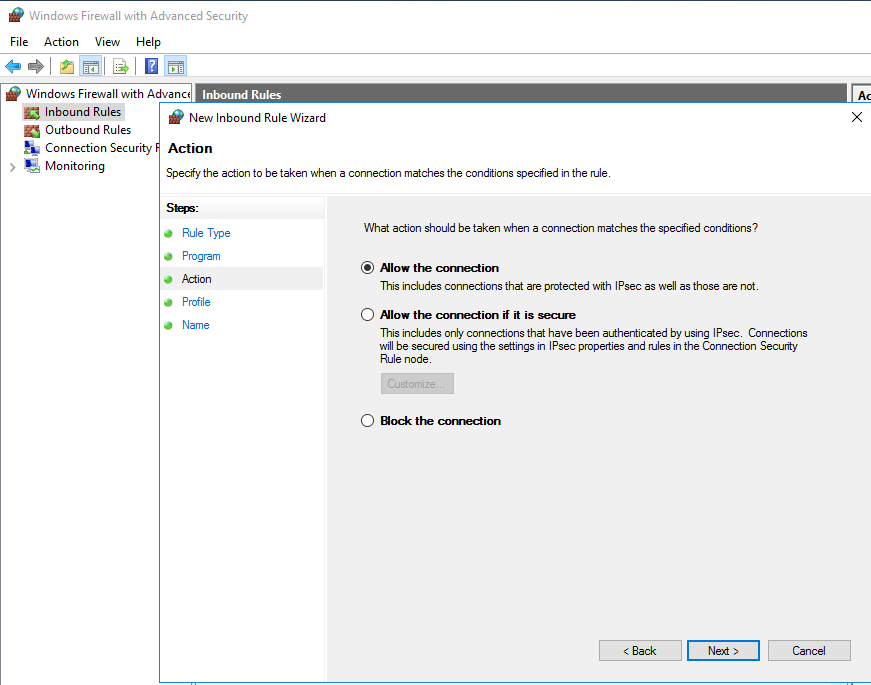
- Next, we select the option “Allow the connection” and then click “Next”.
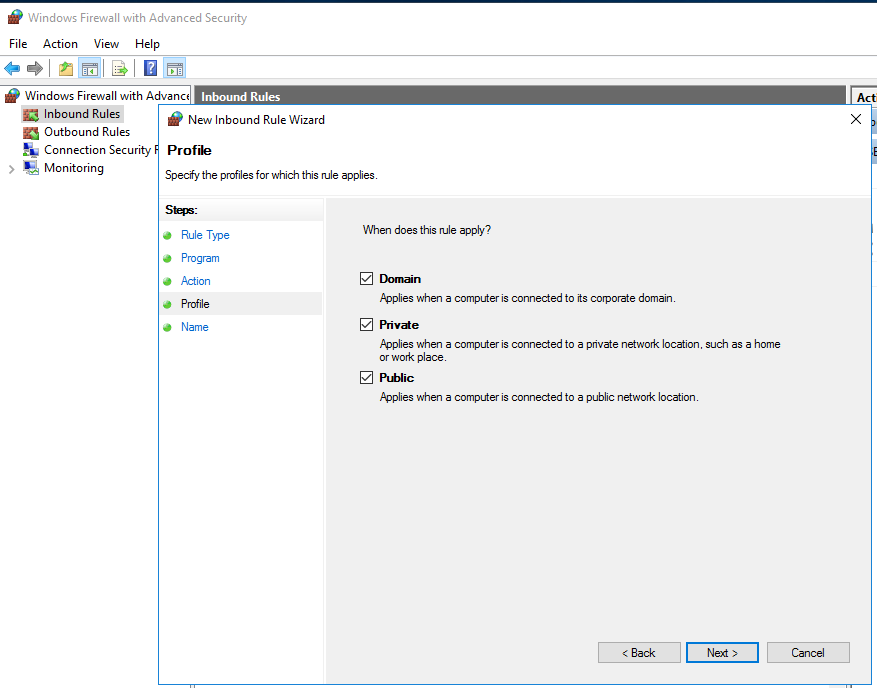
- Select the "Profile" the rule will be applied to and click "Next". (We have allowed all three for demonstration purposes, your selection may vary.)
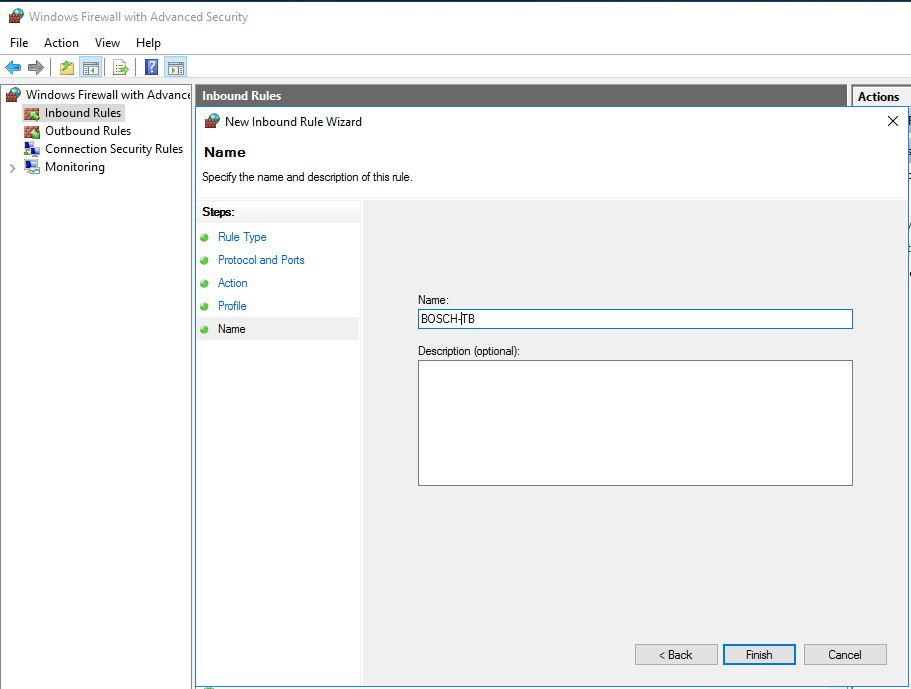
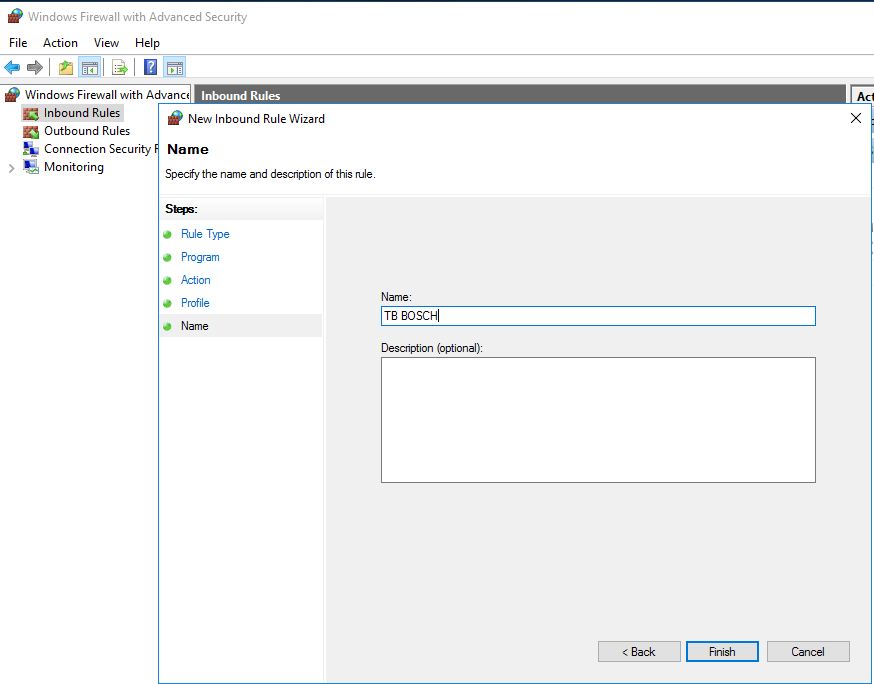
- Select a "Name" and "Description" for this rule and then Click “Finish”.
At this point, you will be dropped back to the main firewall screen. You will now see a new rule in the main firewall rules in the center section, as well as a new listing in the right window pane
Edit a port / program in the firewall
-
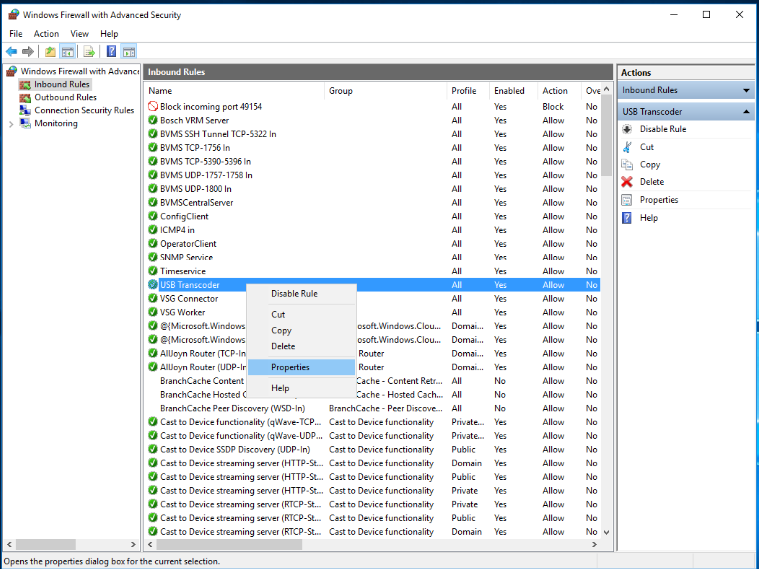
Right-click on the rule which will open a context menu. Then click "Properties" and adjust the rule according your needs.
Close a port / program in the firewall
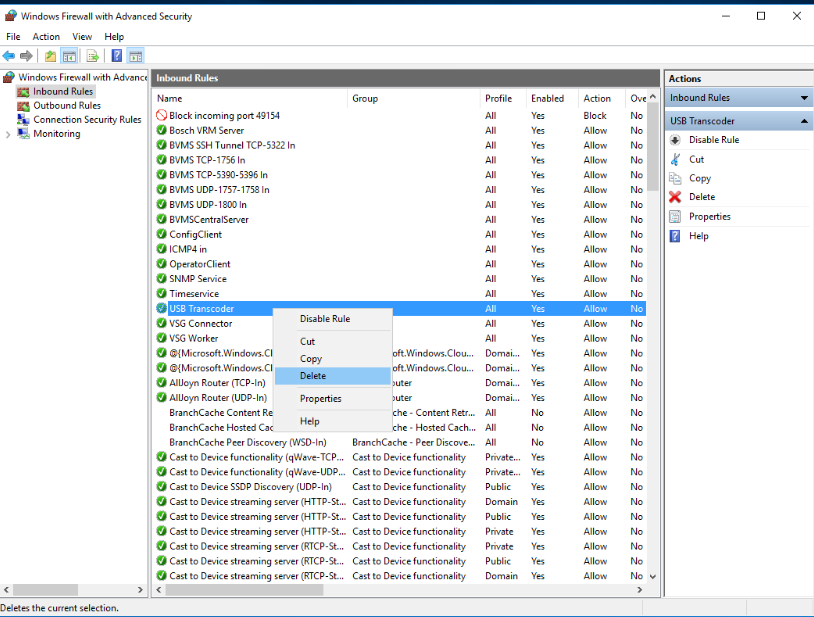
- Right-click on the rule which will open a context menu. Then click "Delete".

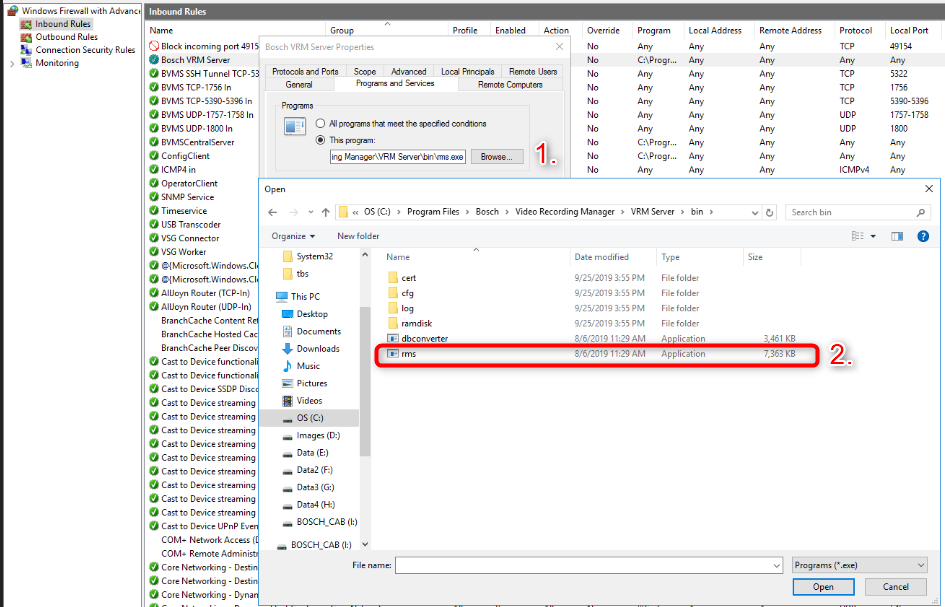
Therefore right-click on the rule which will open a context menu. Then click "Properties" and adjust the programs path to:
- Bosch VRM Server: "C:\Program Files\Bosch\Video Recording Manager\VRM Server\bin\rms.exe"
- USB Transcoder: "C:\Program Files (x86)\Bosch\Video Recording Manager\VRM Server\bin\usbsvc.exe"
Keep in mind, that you need to perform this action on all four rules (inbound and outbound)
Alternatively download the attachment set_fw_rules.zip (1 KB) locally to your device, extract the archive and run the PowerShell script "set_fw_rule_trancoder.ps1" as administrator. The script will adjust all necessary rules.
Still looking for something?
- Top Results